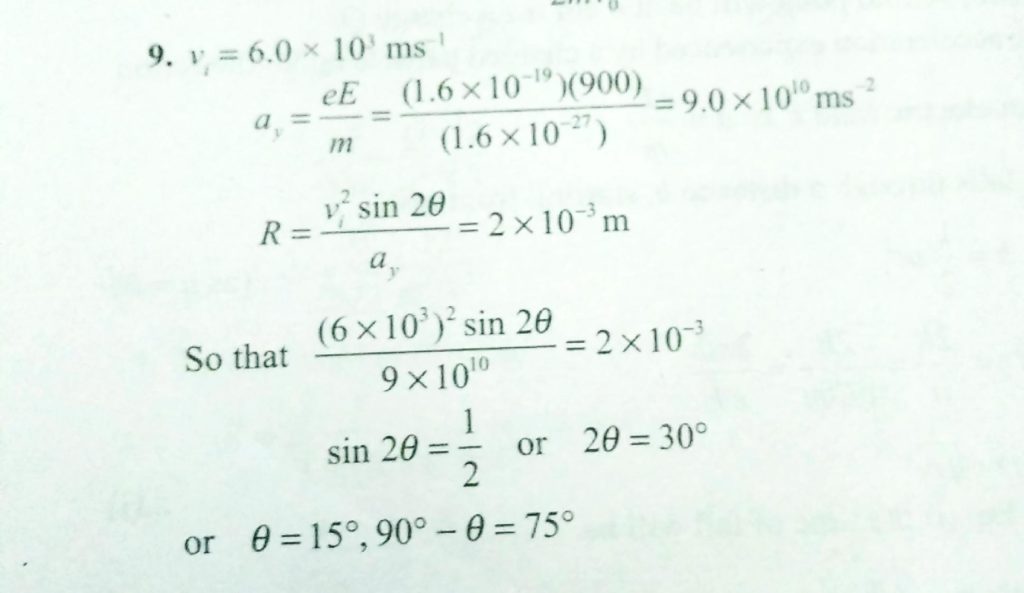Protons are projected with an initial speed vi = 6 km/s from a field-free region through a plane and into a region where a uniform electric field E with arrow = −900 ĵ N/C is present above the plane as shown in in the figure below. The initial velocity vector of the protons makes an angle θ with the plane. The protons are to hit a target that lies at a horizontal distance of R = 1.15 mm from the point where the protons cross the plane and enter the electric field. We wish to find the angle θ at which the protons must pass through the plane to strike the target.