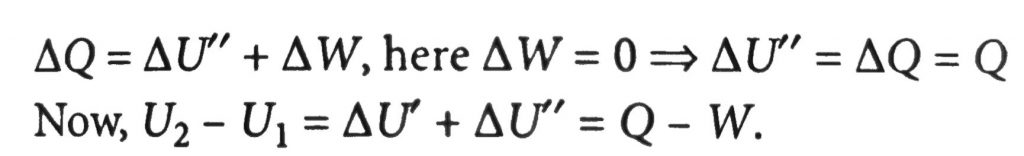A sample of an ideal gas initially having internal energy U_(1) is allowed to expand adiabatically performing work W. Heat Q is then supplied to it, keeping the volume constant at its new value, until the pressure raised to its original value. The internal energy is then U_(2) (see figure). The increase in internal energy (U_(2) – U_(1)) is equal to